Pour Decisions: Understanding Alcohol Overdose Risks
Overview of Alcohol Overdose: Risks and Implications
Definition and Symptoms
Alcohol overdose, also known as alcohol poisoning, is a severe medical condition that arises when a person consumes a significant amount of alcohol in a relatively short timeframe, overwhelming the body’s ability to process it. This excess alcohol can disrupt critical brain functions that regulate essential life-support activities, such as breathing and heart rate, leading to dire consequences. Symptoms indicative of an alcohol overdose include mental confusion, which might manifest as an inability to think clearly or respond to questions, along with vomiting, seizures, and a dangerously low body temperature. The individual’s breathing may become slow, irregular, or even stop, further compounding the health risks. If not promptly treated, alcohol overdose can result in permanent brain damage, a coma, or death, underscoring the urgency of responding to these symptoms.
Understanding the symptoms and risks associated with alcohol overdose is crucial for timely intervention. For instance, individuals who are new to drinking or have pre-existing medical conditions often have a lower tolerance to alcohol, making them more susceptible to overdose. A real-world example includes college students who might engage in binge drinking during parties, unaware of their limits or the rapid impact of alcohol on their bodies. This demographic is particularly at risk, as they may not recognize the early signs of overdose in themselves or their peers, delaying necessary medical intervention. Therefore, education and awareness about these symptoms are essential in preventing and addressing alcohol overdose effectively.
Understanding Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC)
Role of BAC in Impairment
Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) is an essential metric used to determine the concentration of alcohol in an individual’s bloodstream, which is directly related to their level of impairment. A BAC of 0.08% is widely recognized as the threshold for binge drinking, generally reached after consuming about four drinks for women and five for men within a two-hour period. Such levels of BAC are associated with a significant increase in the risk of harmful consequences, including accidents, acts of violence, and even fatalities. For instance, a person with a BAC above this limit may experience slowed reaction times, impaired judgment, and reduced motor skills, all of which can contribute to dangerous situations.
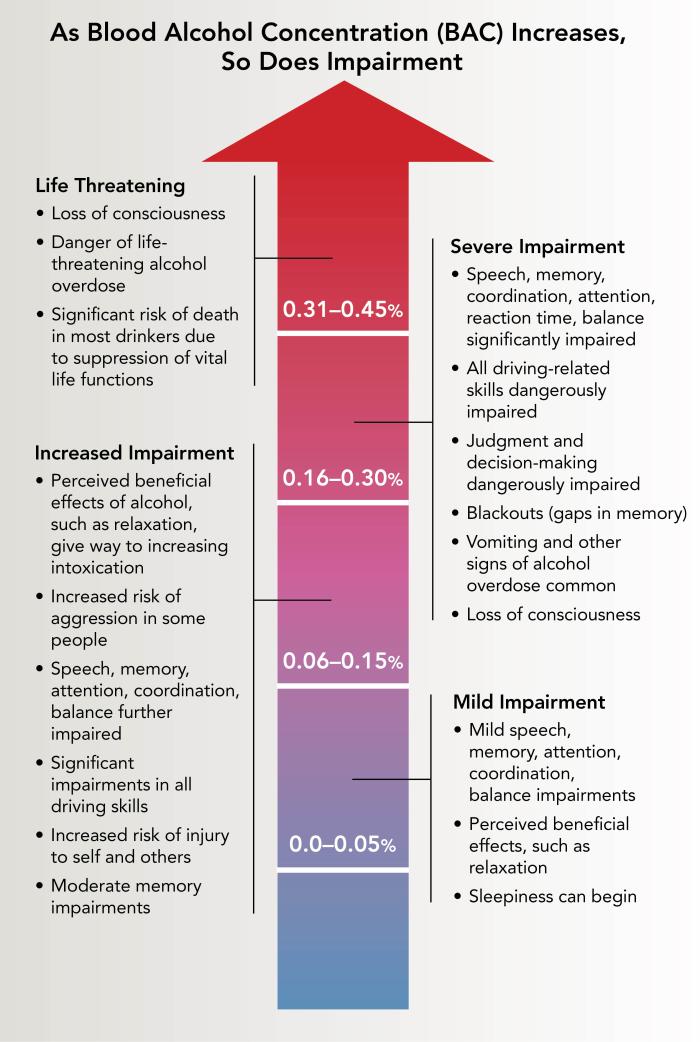
The impact of BAC can vary based on individual tolerance levels, which can sometimes obscure the outward signs of impairment. For example, a person who regularly consumes alcohol may not exhibit obvious signs of intoxication at a higher BAC compared to someone with a lower tolerance. However, this does not mitigate the inherent risks associated with elevated BAC levels. Regardless of perceived tolerance, the physiological effects on critical brain functions remain, such as impaired decision-making and coordination, which are crucial for safe activities like driving. Therefore, it is essential to understand that high BAC levels pose serious risks, emphasizing the importance of adhering to safe drinking practices to prevent potential harm.
 Statistics on Alcohol Overdose and Related Emergencies
Statistics on Alcohol Overdose and Related Emergencies
Data and Trends
Alcohol overdose and related emergencies are alarmingly prevalent, especially among binge drinkers and young adults who are more likely to engage in risky drinking behaviors. This demographic is particularly vulnerable due to the social pressures and the perception of invincibility often associated with youth, leading to higher rates of binge drinking. For instance, college students might participate in drinking games or parties where alcohol consumption is encouraged, significantly increasing their risk of overdose. Such activities can lead to severe consequences, including alcohol poisoning, which can result in catastrophic health outcomes like brain damage and even death [4].
Statistics reveal the severity of alcohol overdose as a public health concern. In the United States alone, approximately 2,200 individuals lose their lives to alcohol poisoning annually, a staggering figure that highlights the deadly potential of excessive alcohol consumption. These numbers underscore the critical need for increased public awareness and preventive measures. Moreover, the trend of alcohol-related emergencies continues to strain healthcare resources, as emergency departments frequently encounter cases of acute alcohol intoxication among young adults. This situation not only endangers lives but also emphasizes the urgency of addressing binge drinking culture and promoting safer drinking practices.
The Importance of Responsible Drinking
 Especially During Holidays
Especially During Holidays
The festive atmosphere of holidays often leads to an increase in social gatherings where alcohol is consumed, sometimes in excess, which significantly elevates the risk of alcohol overdose. This is why responsible drinking becomes especially critical during these times. Adhering to established safe drinking limits helps mitigate the dangers associated with excessive alcohol consumption. For instance, the dietary guidelines suggest that men should limit their intake to two drinks per day and women to one drink per day to prevent adverse health effects. However, during holidays, people may feel tempted to exceed these limits, making it essential to remain vigilant about one’s consumption habits.
Moreover, education and awareness about alcohol risks play a vital role in preventing overdose incidents during holidays. Campaigns that highlight the potential dangers of binge drinking and alcohol overdose can be effective in encouraging individuals to drink responsibly. Additionally, setting personal limits before attending social gatherings can be a practical strategy. For example, deciding in advance not to exceed a certain number of drinks can help individuals keep track of their alcohol intake, thus reducing the likelihood of intoxication and its associated risks. By promoting responsible drinking habits and fostering a culture of moderation, we can safeguard ourselves and others during the festive season.
Immediate Actions for Suspected Alcohol Overdose
Steps for Intervention
When faced with a suspected alcohol overdose, the first and most crucial step is to call 911 without delay. By contacting emergency services, you provide the affected individual with the best chance of receiving prompt medical attention, which is crucial for their survival and recovery. When speaking with emergency responders, it is important to give them as much information as possible about the type and amount of alcohol the person consumed, as well as any other substances that might have been involved. This detailed information can aid medical professionals in determining the most appropriate treatment.
While waiting for help to arrive, take immediate steps to ensure the affected person’s safety. If the individual is vomiting, position them upright or turn their head to the side to prevent choking, a common risk due to the suppression of the gag reflex by alcohol. Never leave an unconscious person alone—doing so can increase the risk of choking or further complications. Avoid attempting to induce vomiting, as this can cause additional harm. Instead, continuously monitor their breathing and pulse. In cases where the person is not breathing or has no pulse, be prepared to perform CPR, as these actions can be life-saving until professional help arrives.
Long-term Effects and Seeking Help
 Consequences and Recovery
Consequences and Recovery
Chronic alcohol abuse can inflict serious and lasting damage on a person’s health, particularly affecting the brain, liver, and cardiovascular system. The potential for permanent brain damage is significant, which can result in cognitive impairments, memory loss, and difficulties in coordination [1]. Furthermore, the risk of developing an addiction is heightened with continued excessive alcohol consumption, leading to a cycle of dependency that can be challenging to break without professional assistance. For example, individuals who engage in frequent binge drinking may find themselves unable to control their drinking habits, which spirals into alcohol use disorder, requiring structured intervention and rehabilitation [1].
Seeking help for alcohol-related disorders is a vital step toward recovery, and numerous resources are available to assist those in need. SAMHSA’s National Helpline offers a confidential and free service that connects individuals with local treatment centers and support systems tailored to their needs. Treatment for alcohol overdose often involves immediate medical interventions such as the administration of intravenous fluids and oxygen therapy to stabilize the individual. Additionally, engaging in support groups can provide ongoing encouragement and guidance throughout the recovery process. It is crucial to note that timely intervention not only enhances recovery outcomes but also significantly reduces the risk of recurrent overdose incidents, thereby promoting long-term sobriety and improved health.
Prevention Strategies for Alcohol Overdose
 Measures to Avoid Overdose
Measures to Avoid Overdose
Preventing alcohol overdose is crucial, and one of the primary strategies involves drinking in moderation. This means adhering to recommended alcohol consumption guidelines, such as limiting intake to one drink per day for women and two for men, as outlined by dietary guidelines. This approach helps maintain blood alcohol concentration at safer levels, reducing the risk of severe impairment or overdose. Moreover, avoiding consuming alcohol on an empty stomach is important, as food can slow the absorption of alcohol into the bloodstream, giving the body more time to process it and reduce peak blood alcohol levels.
Education plays a vital role in prevention efforts, particularly for young adults and teenagers who are more susceptible to binge drinking due to peer pressure and social influences. By providing accurate information about the dangers of binge drinking, such as the increased risk of accidents and alcohol poisoning, young people can make informed decisions about their alcohol consumption. Additionally, it is critical to avoid mixing alcohol with certain medications, like sedatives and painkillers, which can dangerously enhance alcohol’s depressive effects on the central nervous system. Encouraging the use of designated drivers or rideshare services not only promotes personal safety but also protects others on the road, making it a community-wide prevention strategy. These measures collectively contribute to lowering the incidence of alcohol overdose and its associated health risks.

Alcohol and Holidays: A Closer Look
 Cultural and Social Influences
Cultural and Social Influences
Holidays are occasions often marked by celebration and festivity, which can inadvertently lead to increased alcohol consumption. Social gatherings during these times can create environments where peer pressure plays a significant role in influencing individuals to drink more than they normally would. For example, events like New Year’s Eve parties or holiday office gatherings often include alcohol as a central part of the celebration, making it difficult for individuals to moderate their intake amidst the festive atmosphere. It becomes crucial, therefore, to implement strategies that ensure safety, such as designating drivers who abstain from drinking to ensure guests can safely return home, and fostering a culture where friends look out for one another’s well-being to prevent any alcohol-related emergencies.
Additionally, promoting alcohol-free activities during the holidays serves as an effective measure to mitigate the risks associated with excessive drinking. Organizing events that focus on shared experiences rather than alcohol can provide an alternative for those looking to enjoy the festivities without the pressure to consume alcohol. For instance, hosting a holiday movie night or a festive potluck can create a welcoming atmosphere that emphasizes connection over consumption. Moreover, awareness campaigns during holiday seasons play a pivotal role in educating the public about safe drinking practices and the dangers of alcohol overdose. These campaigns can disseminate valuable information on the consequences of binge drinking, thereby encouraging individuals to adopt responsible drinking behaviors during celebrations.
Understanding Alcohol Addiction and Withdrawal
Signs and Support
Alcohol addiction is a chronic disorder that often stems from prolonged and excessive alcohol use, which can escalate to life-threatening situations such as alcohol overdose if left untreated. The addiction not only affects the individual’s physical health but also disrupts their mental and emotional well-being. Professional intervention is crucial in managing addiction and mitigating its severe consequences. For example, rehabilitation centers provide structured environments where individuals can receive medical treatment and counseling, helping them to break the cycle of addiction while addressing underlying psychological issues.
Withdrawal from alcohol can be a daunting process, with symptoms that may range from mild to severe, including anxiety, tremors, and severe cravings. These symptoms can be physically and mentally taxing, often necessitating medical supervision to ensure safety and effectiveness in overcoming the dependency. Support systems are indispensable during this period. Family involvement and counseling create a network of encouragement and accountability, which can be pivotal in an individual’s recovery journey. Recognizing the signs of alcohol addiction early, such as neglect of personal responsibilities, increased consumption, and withdrawal symptoms when not drinking, can empower individuals to seek help before the situation escalates to a critical point.