Bumps on the Road: Navigating Head Trauma Diagnosis via CT
Overview of CT Scans for Head Injuries
Importance of CT Scans
CT scans are pivotal in diagnosing head injuries by providing detailed three-dimensional images of the brain and skull, which help identify structural issues such as fractures and potential neurosurgical needs. They are crucial for ruling out severe complications like bleeding or swelling, which may require immediate medical intervention. For instance, in cases of traumatic brain injuries, timely CT scans can significantly improve treatment outcomes by allowing rapid medical decisions in emergency situations.
The use of CT scans is especially important when quick diagnosis is necessary to manage head trauma effectively. For example, if a patient presents with severe symptoms such as seizures or prolonged unconsciousness, a CT scan can swiftly determine the extent of the injury, aiding in immediate treatment. This rapid assessment is vital in preventing further complications and ensuring the best possible care.
Understanding the PECARN Rule
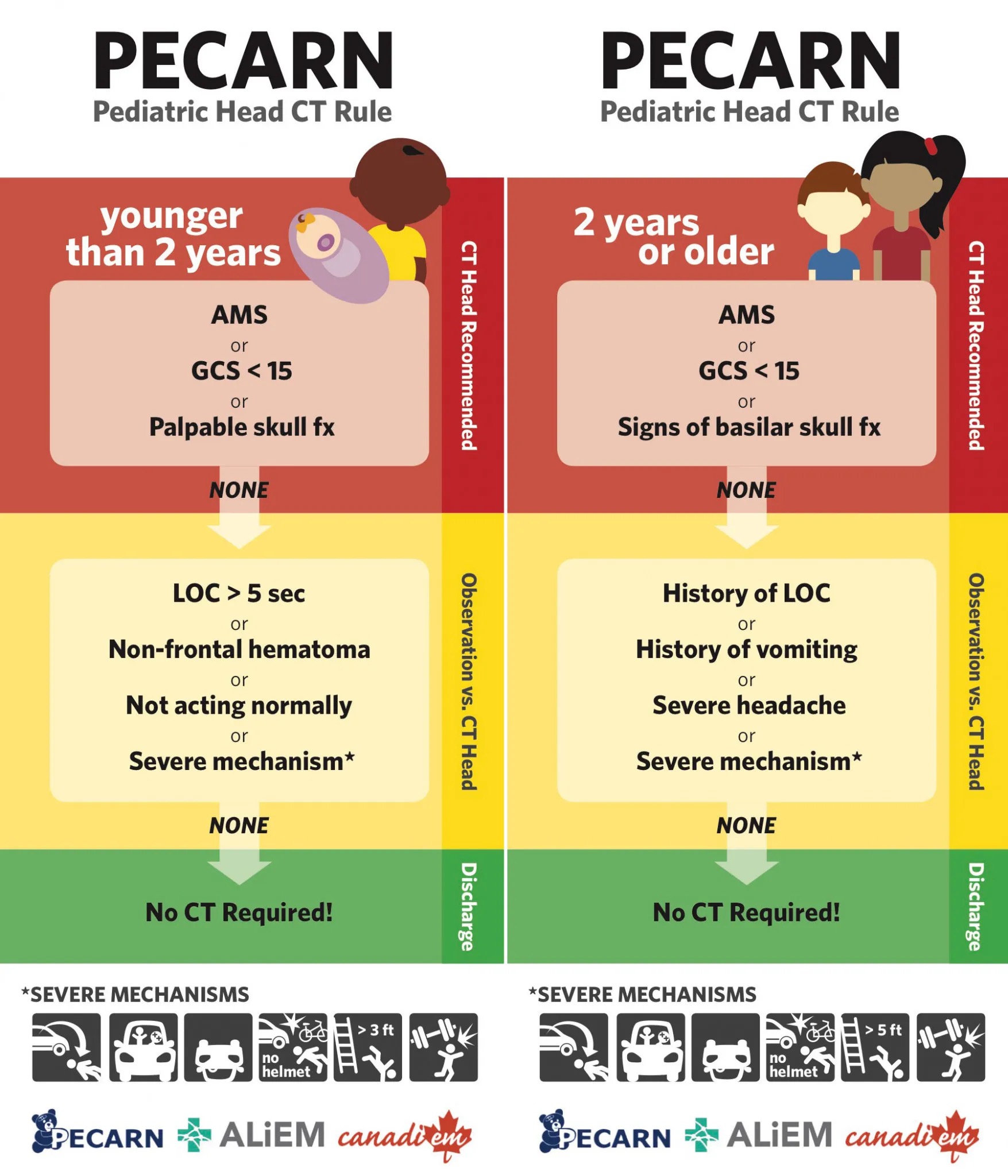
Application in Pediatric Patients
The PECARN rule is a clinical decision guideline used to assess the necessity of CT scans in pediatric head injuries, aiming to minimize unnecessary radiation exposure to children. This rule considers various factors, including the child’s age, the mechanism of injury, and symptoms like vomiting or severe headaches. For example, a child who has sustained a head injury from a fall but exhibits mild symptoms may not require a CT scan, thanks to the PECARN rule’s guidance.
Developed through extensive research, the PECARN rule has been effective in reducing CT scan utilization without compromising safety. It ensures scans are performed only when necessary, thus protecting children from the potential long-term risks of radiation exposure. In emergency departments, applying the PECARN rule also aids in better resource allocation, allowing healthcare providers to prioritize cases that genuinely require immediate imaging.
 Symptoms Indicating the Need for a CT Scan
Symptoms Indicating the Need for a CT Scan
Common Indicators
Certain symptoms are strong indicators of the need for a CT scan following a head injury. These include severe signs such as seizures, prolonged unconsciousness, skull tenderness, sudden severe headaches, nausea, vision problems, slurred speech, and repeated vomiting [1]. For instance, a person experiencing persistent nausea and vision issues after a head impact should undergo a CT scan to rule out serious conditions like bleeding or swelling within the brain.
Individuals on blood thinners or those with a higher risk of skull fractures may also require a CT scan, as their risk of complications is elevated. It’s important to note that symptoms may not always manifest immediately and can develop over hours or days following the injury. Therefore, healthcare providers must remain vigilant for any subtle changes in behavior or cognition that could indicate a serious head injury.
Risks and Guidelines for CT Scans
 Risks, Especially for Children
Risks, Especially for Children
While CT scans are invaluable for diagnosing head injuries, they do expose patients to radiation, which can increase cancer risk over time—a particular concern for children. To mitigate these risks, guidelines recommend limiting CT scans in cases of minor head injuries. Over the past two decades, the use of CT scans for minor head injuries has increased, prompting a reevaluation of current guidelines to avoid unnecessary radiation exposure.
The risk of requiring surgery for a serious injury is less than 1 in 7000 if no severe symptoms are present, underscoring the importance of careful assessment before opting for a CT scan. Monitoring imaging utilization and diagnostic yield is essential to ensure that CT scans are used judiciously, balancing the need for accurate diagnosis with the potential risks of radiation.
CT Scans in Sports-Related Head Injuries
Specific Considerations
In sports-related head injuries, CT scans are typically used for severe symptoms or when other risk factors, like skull fractures, are present. Concussions, a common sports-related head injury, are usually not visible on CT scans. Therefore, immediate medical evaluation after a significant impact is crucial to determine if a CT scan is necessary.
For example, an athlete showing signs of a concussion should be removed from play and evaluated before returning to sports. Education on recognizing head injury symptoms is essential for coaches, players, and parents to ensure timely and appropriate medical care. Understanding these guidelines helps enhance safety and prevent long-term consequences from untreated head injuries.
Final Thoughts on CT Scans for Head Injuries
Steps After a Head Injury
After a head injury, it is critical to seek immediate medical attention to assess the need for a CT scan based on the severity of symptoms and risk factors. Rest and avoidance of strenuous activities are recommended to aid recovery, along with following medical advice. Ongoing monitoring and follow-up with healthcare providers are crucial if symptoms persist or worsen, ensuring prompt intervention if needed.
Patients and caregivers should be educated about the signs of deterioration that necessitate urgent care, such as worsening headaches or changes in consciousness. In sports settings, developing a comprehensive plan for handling head injuries can significantly enhance safety and awareness, ensuring athletes receive the care they need promptly.


